How to Read a W-2 Earnings Summary
The parts of a w2 can be confusing in looking at your income statement for the year. The parts of your W-2 form can seem confusing at first, it consists of many codes, boxes, and numbers.
But after you’ve gotten the knack of filling it in, then filing your W2’s can become like second nature to you.
What is a W-2 earnings summary?
Your W-2 is an earnings statement from an employer and it is a vital part of completing your taxes. In effect, it shows the larger picture of how your employer has paid you throughout a given tax year and what taxes and other payroll remittances are withheld from your gross pay.
To recap, here are some of the basic parts of a W2
• Your SSN or Social Security Number
• Your Employer’s EIN or employer identification number
• Names and addresses of employee and employer
• Gross pay
• Taxes withheld
How many W-2 forms will I receive?
You may receive more than one w2 form. If you had more than one wage paying jobs, you can expect W-2’s from each of the employers you have. In fact, it is the yearly obligation of employers to send the W2 forms to each of their workers to accomplish their filing.
If your previous employer paid you more than $600 or if they paid you a certain amount and withheld tax.
You ought to get 3 copies of each w2 you’re given.
Copy B is given as the federal tax return.
It is filed with your state.
Copy C is given for your personal records.
Copy A is what your employer will send to the SSA or social security administration
Copy D is for employers to keep for themselves.
Will I get a W2 if I am self employed?
If you’re self employed, you may get a tax form called 1099-MISC from organizations whom you received non wages form of payment. However, you need a Form 1040 if you’re filing individual income tax returns.
1099 is a supplemental form, you use the information on your 1099-MISC to fill in your tax information for individual returns on your Form 1040.
What are the parts of a W-2?
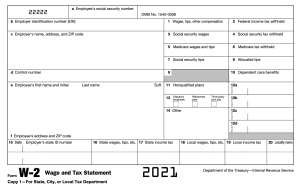
Each part in the w2 contains vital information which is related to tax returns. We’ll go over each box to make sure that you understand it’s purposes and contents.
Box A
This is where you put your Social Security number. Your SSN is the how IRS identifies you.
Box B
EIN, the employer identification number is the official record of the IRS of your employer.
Box C
Your employer’s name, address and ZIP code.
Box D
Employers may choose to include a code in this section to identify your form.
Box E
Your full and legal name
Box F
Your address and ZIP Code
Box 1
This is the total amount of taxable wages. It also has tips, and other taxable compensation your employer paid.
This does not include any money you deferred such as benefits including your 401(k) plan or your IRA pension.
Box 2
Federal taxes your employer has withheld from your wages.
Box 3
The total wages which are then remitted to Social Security. Certain income may be subject to your SSN but it is not income tax. It may be higher than box 1.
Box 4
Social Security taxes withheld on wages and tips. For instance, in 2019, the maximum amount of wages that Social Security tax can withhold is $132, 000, this amount is called the social security wage base limit. You won’t have to pay SS wages if you earn excess of that.
The Social Security tax rate typically is around 6.2% and it must not exceed $8239.80.
Box 5
Total wages and tips which you report to your employer. Medicare taxes then are deducted from this amount. Medicare taxes howver, have no wage limit. This number may be larger than that of Box 1 or Box 3.
Box 6
Medicare taxes withheld for your tax year. Since there is no wage base limit, the Medicare tax rate is at 2.9% - 1.45% from employees and then 1.45% for employers and this applies to all earnings too.
Box 7
These are the tips you report to your employer. If you leave this box blank, then you may not receive tips or you may have unreported tips you need to declare.
Box 8
If you work for a large company in food and beverages, they may pool the tips of their employees. This is for employers to report the tips which are allocated to you.
Box 9
This is a verification code. It can be left alone if your employer is not participating in the IRS pilot program.
Box 10
The amount of dependent care benefits you chose. If you deferred certain amounts to pay for dependent care or if your employer pays for these amounts, then those funds are going to be shown here.
Box 11
This is payment from a non-qualified deferred compensation plan. This is to show the Social Security Administration if parts of box 1 or 3 and 5 were earned in previous year and it can then verify the right amount of benefits to be paid.
Box 12
These include all the codes your employer will report to IRS. There are lots of items your employer ought to report here. These include non taxable sick pay or moving reimbursements for the armed forces.
Box 13
Statutory employee status – these are your earnings which are subject to Social Security and Medicare taxes but these are not subject to federal income tax withholding.
Retirement plan – You were an active participant in a retirement plan e.g. 401(k) in the past year
3rd party sick pay – you got sick pay through an insurance provider.
Box 14
Your employer reports anything which can include nontaxable income, union payments and uniforms including health insurance premiums.
Box 15 to 20
State and local income tax information reported. If state information is included here, you still must not forget to attach Copy 1 to any state, city or local tax return if you are not required to submit.
What should I do with my w2?
If you have an understanding of the gist of w2, then you may now use it to complete your federal and state income taxes.
It’s also a great idea to start generating pay stubs if you are self-employed. This makes it easier to track your earnings at any given period in the tax year.
Related Content
How long should I keep my W-2 for?
3 – 7 years is the ideal period for keeping your tax returns. Yet it can also vary on the documents and the circumstances surrounding your income tax situation.
What if my employer won't give me a w2?
You can contact your employer and then ask for help from the IRS.
What You Can Do Next
You can generate a W-2 Form using our online W-2 Form generator or create a pay stub using our online paystub generator.